定义
拓扑排序是对一个 $DAG$ 图的线性排序算法,满足对于任何一条从 $u$ 到 $v$ 的有向边,都有 $u$ 在 $v$ 的前面
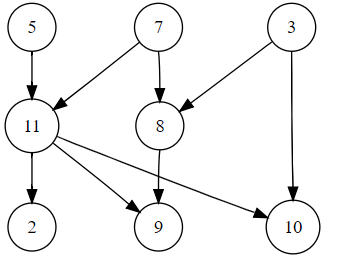
比如,下图的拓扑排序为 $3, 7, 8, 5, 11, 10, 2, 9$ (答案不唯一)
Kahn算法
- 将所有入度为 $0$ 的点插入队列 $S$ 中
- 当队列 $S$ 不为空的时候,去除队首 $x$,将 $x$ 插入数组 $ans$
- 删除所有从 $x$ 出发的有向边
- 检查有无新的入度为 $0$ 的点,插入队列 $S$ 中
- 回到第二步
最后 $ans$ 数组就是这个 $DAG$ 的拓扑排序
L ← Empty list that will contain the sorted elements
S ← Set of all nodes with no incoming edge
while S is non-empty do
remove a node n from S
add n to tail of L
for each node m with an edge e from n to m do
remove edge e from the graph
if m has no other incoming edges then
insert m into S
if graph has edges then
return error (graph has at least one cycle)
else
return L (a topologically sorted order)
例题 Luogu – 1038 神经网络
题目描述
在兰兰的模型中,神经网络就是一张有向图,图中的节点称为神经元,而且两个神经元之间至多有一条边相连,下图是一个神经元的例子:
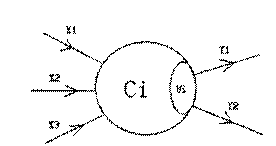
图中,$X_1 – X_3$ 是信息输入渠道,$Y_1 – Y_2$ 是信息输出渠道,$C_1$ 表示是阈值,可是为神经元的一个内在参数。
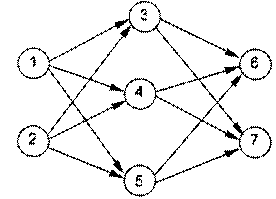
神经元按一定的顺序排列,构成整个神经网络。在兰兰的模型之中,神经网络中的神经元分为几层;称为输入层、输出层,和若干个中间层。每层神经元只向下一层的神经元输出信息,只从上一层神经元接受信息。下图是一个简单的三层神经网络的例子。
兰兰规定,$C_i$ 服从公式:(其中 $n$ 是网络中神经元的数目)
$$C_i = \sum_{j,i \in E} W_{ji}C_j – U_i $$
公式中的 $W_{ji}$ (可能为负值)表示连接 $j$ 号神经元和 $i$ 号神经元的边的权值,当 $C_i$ 大于 $0$ 时,该神经元处于兴奋状态,否则就处于平静状态。当神经元处于兴奋状态时,下一秒它会向其他神经元传送信号,信号的强度为 $C_i$
如此.在输入层神经元被激发之后,整个网络系统就在信息传输的推动下进行运作。现在,给定一个神经网络,及当前输入层神经元的状态 ($C_i$),要求你的程序运算出最后网络输出层的状态。
输入格式
输入文件的第一行是两个整数 $n$ 和 $p$。接下来 $n$ 行,每行 $2$ 个整数,第 $i+1$ 行是神经元 $i$ 的最初状态和阈值,非输入层的神经元开始时的状态必然为 $0$。再接下来 $P$ 行,每行由 $2$ 个整数 $i, j$ 以及 $1$ 个整数 $W_{ij}$,表示连接神经元 $i, j$ 的边权为 $W_{ij}$
输出格式
输出文件包含若干行,每行有 $2$ 个整数,分别对应一个神经元的编号,及其最后的状态,$2$ 个整数间以空格分隔。仅输出最后状态大于 $0$ 的输出层神经元状态,并且按照编号由小到大顺序输出。
若输出层的神经元最后状态均为 $0$ ,则输出 “NULL”。
输入样例
5 6
1 0
1 0
0 1
0 1
0 1
1 3 1
1 4 1
1 5 1
2 3 1
2 4 1
2 5 1
输出样例
3 1
4 1
5 1
解题思路
我们统计每一个点的入度和出度,不难发现出度为 $0$ 的点一定是输出层。
将这幅图进行拓扑排序,对于每一个队首的点 $x$,对反向边全部做题目要求的公式操作,并对 $0$ 取最大值
最后输出结果即可
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 100 + 10;
const int MAXM = 20000 + 10;
int Head[MAXN], to[MAXM], Next[MAXM], w[MAXM], tot = 1;
bool vis[MAXN], flag[MAXN];
int in[MAXN], out[MAXN], ans[MAXN], u[MAXN], cnt;
inline int read(){
int x = 0;
int p = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9'){
if(ch == '-')
p = 0;
ch = getchar();
}
while('0' <= ch && ch <= '9'){
x = x*10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return p ? x : (-x);
}
inline void add(int a, int b, int c){
to[tot] = b;
w[tot] = c;
Next[tot] = Head[a];
Head[a] = tot++;
}
int que[MAXN], l, r;
int n, m;
inline void toop(){
for(register int i=1; i<=n; i++){
if(!in[i]){
que[r++] = i;
vis[i] = true;
}
}
while(l != r){
int x = que[l++];
for(register int i=Head[x]; i; i=Next[i]){
int v = to[i];
if(vis[v]){
ans[x] += ans[v] * w[i];
}else{
in[v]--;
if(in[v] == 0){
que[r++] = v;
}
}
}
if(!flag[x]){
ans[x] -= u[x];
}
ans[x] = max(ans[x], 0);
vis[x] = true;
}
}
int main(){
n = read();
m = read();
for(register int i=1; i<=n; i++){
ans[i] = read();
u[i] = read();
if(ans[i] != 0){
flag[i] = true;
}
}
for(register int i=1; i<=m; i++){
int a = read();
int b = read();
int c = read();
in[b]++;
out[a]++;
add(a, b, c);
add(b, a, c);
}
toop();
bool flag2 = false;
for(register int i=1; i<=n; i++){
if(ans[i] > 0 && out[i] == 0){
printf("%d %d\n", i, ans[i]);
flag2 = true;
}
}
if(!flag2){
puts("NULL");
}
return 0;
}

